EF 2. Electric Field Edited
Last Edit: 3/21/25
Electric Field 电场 #
- 在科学中存在多个 Field的概念,其中包含了 Teperature Field,Pressure Field 等
- 而 Electric Field 则是一个 Vector Field,矢量场,其包含了大小与方向
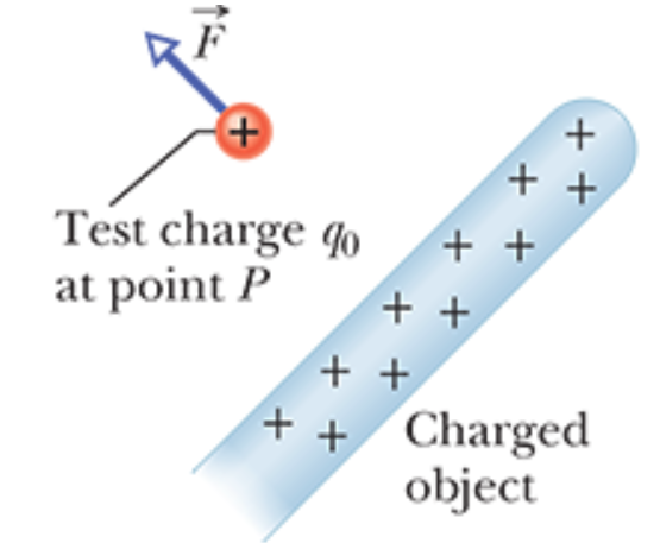
- 具体来说,定义 Electric Field的方式是在 Electric Field \(\vec{E}\) 的某个点 P 处放置一个 Small Positive Charge 的 \(q_0\),其为 Test Charge
We want the charge to be small so that it does not disturb the object’s charge distribution
Electric Field Strength 电场强度 #
- 一个表示电场强弱的物理量
- 电场 \(\vec{E}\) 在点 P 由带电对象产生,对试验电荷 \(q_0\) 产生了静电力 \(\vec{F}\)
- 由于 \(p_0\) 是一个正的Charge,所以电场的方向是电力的方向,而电场的大小有
$$ \vec{E} = \frac{\vec{F}}{q_0} $$
- Electric Field 的国际单位系统 (SI) 单位是牛顿每库仑(N/C)
Electric Field Lines 电场线 #
- 由于需要一种方式可视化电场,Eletric Field Lines出现了
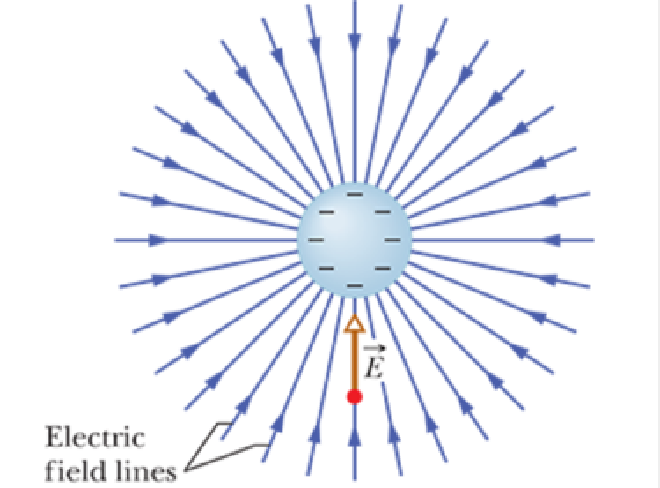
- Electric Field Line 的方向是由正电荷指向负电荷
- 根据 Electric Field 的性质,电场线的密集程度反映了电场的强度。电场线越密集,电场强度越大
ex. Graph Interpretation of Electric Field #
In the figure the electric field lines on the left have twice the separation as those on the right. (a) If the magnitude of the field at A is 39 N/C, what is the magnitude of the force on a proton at A? (b) What is the magnitude of the field at B?

The Electric Field Due to a charged Particle #
- 为了找到 Charged Particle(通常称为点电荷)产生的 Electric Field,我们在粒子距离 r 的位置放置一个正测试电荷
- 前面知道 Coulomb’s Law 有
$$ F = \frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_0} \frac{|q||q_0|}{r^2} $$
- 将 \(\vec F\) 代入到 \(\vec E\) 中便可以得到
$$ \vec{E} = \frac{\vec{F}}{q_0} = \frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_0} \frac{q}{r^2}\quad \text{(charged particle)} $$
Principle of superposition 电场的叠加原理 #
- 如果在某点有多个电荷产生的电场,可以通过叠加原理来计算该点的总电场。文中用到了叠加原理,表达式为
$$ \vec{E} = \vec{E}_1 + \vec{E}_2 + \cdots + \vec{E}_n $$
- 这说明总电场是各个单独电场向量的矢量和
ex. Electric Field Superposition #
In the figure the four particles are fixed in place and have charges \(q_1 = q_2 = 4e\), \(q_3 = 2e\), and \(q_4 = -8e\). Distance d=4.75d = 4.75 µm. What is the magnitude of the net electric field at point P due to the particles?


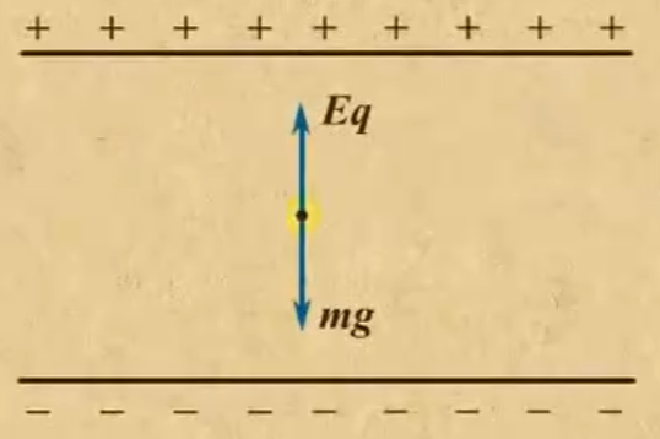
A Point Charge in an Electric Field #
- 当一个 Particle 有着 q 的 Charge 被放置在 Electric Field \(\vec E\) 中的时候,Electric Field 会对其产生\(\vec F=q\vec E\) 的Electrostatic Force
Millikan Oil-drop Experiment #
- 罗伯特·A·密立根在1910年进行的著名实验油滴实验,用于测量电子的基本电荷e