Last Edit: 11/26/24
Set Notation 集合 #
- Set is a collection of objects, called elements of the set $$A={t|t\in R}$$
- 这就是一个矩阵,其中A为t,而t可以取任意Real Number
- 这就是集合的表示方法,用这种方法便可以表示向量,直线和平面
Union of Sets 并集 #
- 对于两个集合,其Union是另一个Set,其元素包含了all elements of A and B $$A \cup B = { x \in X \mid x \in A \text{ or } x \in B }$$
Intersection of Sets 交集 #
- 对于Intersection来说,这个Set包含了任意同时出现在A与B中的元素 $$A \cap B = { x \in X \mid x \in A \text{ and } x \in B }.$$
Vector 向量 #
- 思考一个问题,对于一个坐标轴上的点\((2,1)\)和一个向量\(\vec v =[2,1]^T\),他们的区别
- Point:点是空间中的一个位置,用坐标表示,如P = (x, y, z)表示三维空间中的一个具体位置。点没有方向和大小。
- Vector:向量是一个有大小和方向的数学对象,通常表示两个点之间的位移。例如,从点 A到点B的向量可以表示为\(\mathbf{v} = \overrightarrow{AB}\)
- 亦可以说Point是绝对位置,而向量是一个点到另外一个的有方向的距离
Norm 模 #
- 对于\(\vec{v} = \begin{bmatrix} v_1 \ v_2 \ \vdots \ v_n \end{bmatrix} \text{ be in } \mathbb{R}^n\)
- 它的Norm,也就是向量长度即为 $$\sqrt{v_1^2 + v_2^2 + \cdots + v_n^2}$$
Dot Product 点积 #
- Dot Product,用来衡量两个Vector方向相似程度的一个Scalar
- 其值从-1到1(仅当两个Vector为Unit Vector的情况下),从方向相反,到同方向,在0的时候代表两个Vector Orthogonal 垂直
Definition #
$$\mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{b} = a_1 b_1 + a_2 b_2 + \cdots + a_n b_n = \sum_{i=1}^n a_i b_i$$
- 公式中的每一项\(a_i b_i\)表示两个向量在某个维度上的大小相乘
- 点积实际上是在将a和b的方向分量进行逐一对比,累加得到两个向量在整个空间上的“相似性”,每一个维度的相似性都将累加到最终的空间相似性上
- 想要表达这个相似性,还存在另一种方式,即通过Projection $$\mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{b} = |\mathbf{a}| |\mathbf{b}| \cos \theta$$
- 其代表了b在a方向上Projection的长度再乘以a
Angle Between Vectors #
- 同理可以用Dot Product公式推导两个Vector之间的夹角 $$\theta = \cos^{-1} \left( \frac{\mathbf{A} \cdot \mathbf{B}}{AB} \right) \quad 0^\circ \leq \theta \leq 180^\circ$$
Application #
- Dot Product的一种用法便是Force Vector Directed Along a Line
- 对于一个在\(\vec u\)方向上的Force F,有 $$\vec F_u=\vec F\cdot \vec u=(F\times 1)\cdot \cos\theta=F\cdot \cos\theta$$
- 而这一个\(\cos\theta\)则是 $$\cos\theta=\frac{\vec v\cdot \vec{w}}{|v|\times|w|}$$
- 当把其中一个Vector替换为Direction Vector时,便可以得到Axis-Force’s Direction Cosine $$\cos\theta = \frac{{r_xi+r_yj+r_zk}}{\sqrt{r_x^2+r_y^2+r_z^2}\cdot 1}$$
- 所以就有\(F\cdot \cos \theta=F\cdot \vec u\)之后便可以得到Force在\(\vec u\)方向上的力的Magnitude(注意Dot Product的结果是一个Scalar)
- 要想得到Force在\(\vec u\)方向上的Cartesian Vector,需要再次乘以Direction Vector
最终公式 #
$$\vec F=F_u\cdot \vec u= (\vec F\cdot u\cdot\cos\theta)\cdot \vec u=(F\cdot\frac{{r_xi+r_yj+r_zk}}{\sqrt{r_x^2+r_y^2+r_z^2}\cdot 1})\cdot\vec u$$
Line 直线 #
- 考虑一个问题Consider the two points P = (1, 2) and Q = (−1, 4),find an equation for the line y = mx + b which passes through P and Q
- 通过Point-Point Formula可以算出 $$y_2-y_1=\frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1}(x_2-x_1)$$
- 解得 \(y=−x+3\)
- 现在考虑相似的问题 Suppose x and y satisfy the vector equation $$\begin{bmatrix} x \ y \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 \ 2 \end{bmatrix} + k \begin{bmatrix} 1 \ -1 \end{bmatrix}, \text{ where } k \in \mathbb{R}$$
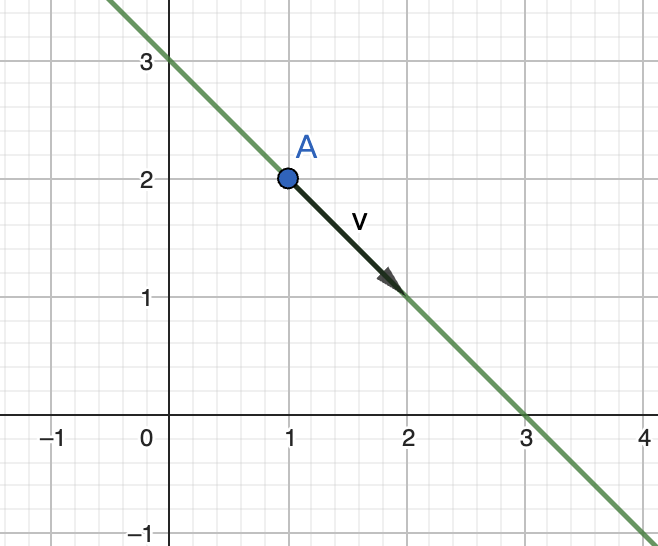
- 可以发现两个不同的形式表达了同一个Line,他们之所以等价是因为
- \([1,2]^T\)是直线上的一个固定点(在直线上)。
- \(k\begin{bmatrix} 1 \ -1 \end{bmatrix}\)是一个方向向量,表示直线的方向(斜率),而方程中的斜率为\(m = \frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}\),用Direction Vector的y分量除以x分量就可以得到一样的结果
- 而对于Intersection来说,当k=-1的时候,有 $$\begin{bmatrix} x \ y \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 \ 2 \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} -1 \ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \ 3\end{bmatrix}$$
- 也就是截距
- 于是就可以定义如下的Line using Set Notation $$L = { \vec{u} \in \mathbb{R}^2 \mid \vec{u} = \vec{v} + t \vec{d}, \text{ for some } t \in \mathbb{R} }$$
为什么需要两个向量 —> 因为需要Position Vector区分不同平行的直线
Plane #
- 同理对于一个Plane,可以通过两个Linearly Independent的Vector与一个Plane上的点表示
- 至于前面Line中所提到的Slope,在这里便是Partical Derivative $$\mathcal{P} = { \vec{u} \in \mathbb{R}^3 \mid \vec{u} = \vec{p} + s \vec{d}_1 + t \vec{d}_2, \text{ for some } s, t \in \mathbb{R} }$$
- 可以发现u是一个\(\mathbb R^3\)中的Subset,这代表了该Subset只含有两个Degree of Freedom,即为三维空间中的一个Plane
注意这里的Plane是一个Subset,不是Subspace,具体原因将在后面指出
Normal Vector #
- 对于平面\(Ax+By+Cz=D\)来说,其Normal Vecotr,也就是垂直于整个Plane的Vector即为\(n=[A,B,C]^T\)
Proof #
- \(P(x_1,y_1,z_1)\)和\(Q(x_2, y_2, z_2)\)都在平面上,那么它们的坐标满足平面方程 $$Ax_1+By_1+Cz_1=D,Ax_2+By_2+Cz_2=D$$
- 则可以构建向量\(\vec{v} = \begin{bmatrix} x_2 - x_1 \ y_2 - y_1 \ z_2 - z_1 \end{bmatrix}\)
- 结合方程组则有\(A(x_2-x_1)+B(y_2-y_1)+C(z_2-z_1)=0\)
- 也就是\(\vec v \cdot \vec n =0\),其中\(\vec{n} = \begin{bmatrix} A \ B \ C \end{bmatrix}\)
Second definition #
- 结合上面的思想便可以得到Space的第二个Set Notation表达式 $$\mathcal{P} = { \vec{u} \in \mathbb{R}^3 \mid \vec{n} \cdot (\vec{u} - \vec{p}) = 0 }$$
- \(u∈R^3\):表示平面上的任意点的坐标。
- \(\vec{n} \in \mathbb{R}^3\):表示平面的法向量,即垂直于平面表面的向量。
- \(\vec{p} \in \mathbb{R}^3\):表示平面上的一个固定点,用于确定平面的具体位置。
- 点积\(\vec{n} \cdot (\vec{u} - \vec{p}) = 0\):表示向量\((\vec{u} - \vec{p})\)与法向量\(\vec{n}\)正交。
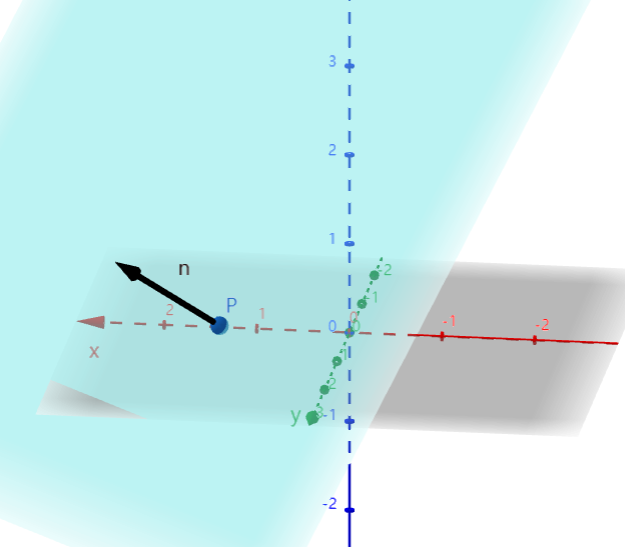
- \(\vec p\)为Plane上一点,\(\vec n\)为Plane的Normal Vector,剩下的就是点上的任意位置了,由于任意\(\vec u\)都在平面中,\(\vec u-\vec p\) 将仍处于Plane中,而\(\vec n⋅(\vec u−\vec p)=0\)是限定他的条件
所有的Vector都为Position Vector,即以坐标系Origin为Head的Vector
ex. #
-
Find the equation for a plane \(\mathcal{P}\) which contains the three points P = (0, 1, 1), Q = (2, 0, 4), andR = (0, 0, 1)
-
Express \(\mathcal{P}\) in vector form, in normal form, and as an equation ax + by + cz = d
-
用三个点确定Plane上的两个Vector
$$\vec{v}_1 = \begin{bmatrix} 2 - 0 \\ 0 - 1 \\ 4 - 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ -1 \\ 3 \end{bmatrix}$$
$$\vec{v}_2 = \begin{bmatrix} 0 - 0 \\ 0 - 1 \\ 1 - 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ -1 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix}$$