Last Edit: 1/13/25
In this chapter, we will discuss how to make decisions in C. We will discuss the if, else and else if statements
3.1 If-Statement #
- 开发一个提示用户输入年龄的程序。如果未满工作的法定年龄,程序会打印“您还没有资格工作”,否则会显示“您有资格工作”
if和else的语法在C中如下
if (condition) {
// code to execute if condition is true
} else {
// code to execute if condition is false
}
3.1.1 What can this condition be #
- Condition是一个Bool variable,其可以用
True表示,也可以用Numerical Value。在C中,任意非零的值都(通常用1)代表了True,而False则是0
Relational Expression #
- 关系运算符通常使用以下的符号
==:Equal to!=:Not Equal to<:Less than>:Greater than<=:Leq>=:Geq- 有了这些就可以完整编写一个判断年龄的程序了
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
int age = 0;
printf("Enter your age: ");
scanf("%d", &age);
if (age < 14) { // Condition
checking if age is less than 14
printf("You are not yet
eligible to work in Ontario.");
} else {
printf("You are eligible to
work in Ontario.");
}
return 0;
}
3.1.2. What can we do with relational operators? #
- 通过Relational Operators,可以实现
- 比较值的大小:
(7.2>5.1) - 比较
char的大小:'a'>'b',这里比较的是他们的ASCII - 比较
char和int:比如(0 == '0'),char的0有ASCII = 48,所以0 != ‘0’
int x = 0;
if (x = 1) {
printf("True");
}
- 这是一个判断,他最终会输出True,这是因为即使第一行赋值
int x = 0;,第二行重新令x = 1,使得判断变成了if (1),而1就是True
3.2 Multiple Conditions #
- 想要同时判断两个Condition的成立,可以通过
&&的判断符,这些完整的叫做Logical Operators
3.2.1 Logical/Boolean Operators #
| A | B | A && B | A || B |
|---|---|---|---|
| false | false | false | false |
| false | true | false | true |
| true | false | false | true |
| true | true | true | true |
- 完整的Logical Opeators的判断结果如上,但是记住过程比背下表格更加简单
&&,and,当A和B同为true则为True,其他均为False||,or,当A和B其中一个为True则整体为True- 还有第三个Logial Operators为
!,其的作用就是Reverse Bool Value
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
char letter = ' ';
printf("Enter a letter: ");
scanf("%c", &letter);
if (letter == 'A' || letter == 'a') {
printf("You entered an upper case or lower
case A.");
} else {
printf("You did not enter an upper case or
lower case A.");
}
return 0;
}
- 上面的程序,当输入为A或者a的时候,都会进入if,因为用的是
||,or判断符
3.2.1.1 Lazy Evaluation #
- 假设执行了
x % y < 10的判断,一个问题可能出现在当y=0的时候,所以这就需要在整除之前做一步y!=0的判断 - 一种做法就是nested-if,嵌套if,这是一个非常lj的做法,虽然可读性高,但占用的时间和空间都是庞大的
if (条件1) {
// 条件1满足时执行的代码
if (条件2) {
// 条件1和条件2同时满足时执行的代码
}
}
- 另外一种做法就是通过Lazy Evaluation,其实就是使用
&&
if (y != 0 && x % y < 10) {
// do something
}
- Lazy evaluation将多个判断结合为一个的办法,详细来说他会从左到右的顺序判断
||- 这个运算符先评估左侧的表达式(LHS,Left-Hand Side)。
- 如果LHS为
true,那么整个条件表达式结果为true,程序将不再继续评估右侧的表达式(RHS,Right-Hand Side)。 - 如果LHS为
false,程序需要继续评估RHS来决定整个表达式的结果。 &&- 这个运算符也先评估LHS。
- 如果LHS为
false,那么整个条件表达式结果为false,程序将不再继续评估RHS。 - 如果LHS为
true,程序需要继续评估RHS来决定整个表达式的结果。 - 这种评估方式是一种效率优化手段,可以减少不必要的计算
3.2.1.2 De Morgan’s Law #
- 当一个Lazy Evaluation(注意仅是两个及以上的判断同时发生的情况下)判断的最外侧为一个Not,也就是
!的时候,整体的判断将会看上去十分复杂,这可以通过De Morgan’s Law化简 - 具体来说
!(A && B)is equivalent to!A || !B,!(A || B)is equivalent to!A && !B - 同时Relational Expression也可以变换,> 变成了<=,>= 变成 <,== 变成 !=
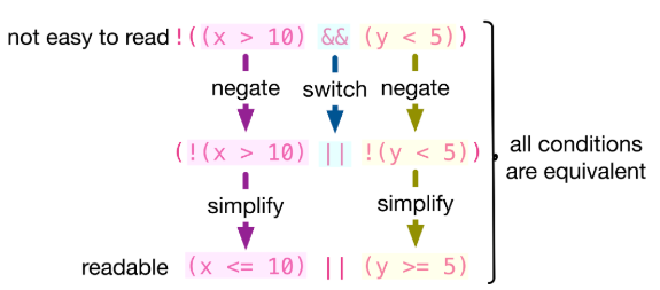
3.3 Nested-if Statement #
- 当想要做特别多的判断的时候,可以采取Nested-if Statement,也就是嵌套If
3.3.2 Dangling Else Problem #
- 在C语言中,
if语句可以不带大括号{}来执行单条语句
if (condition)
statement;
else
statement;
- 这种写法没有问题,因为每个
if和else清晰地对应一条语句。但是,如果没有使用大括号对嵌套的if语句进行清晰的界定,就会产生 Dangling Else 问题
if (condition1)
if (condition2)
statement;
else
statement;
- 在这种情况下,不明确的是这个
else应该属于哪个if。按照C语言的规则,else总是匹配最近的未匹配的if,所以在没有大括号明确界定的情况下,上面的else属于if (condition2) - 所以没事就加个
{}