Last Edit: 1/8/25
1.2 Binary representation in memory #
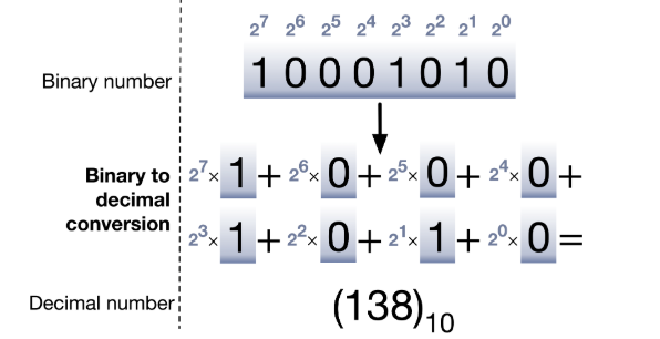
Binary to Decimal Number 二进制转十进制 #
- Binary到Decimal Number的转换通过位数和值相乘得到
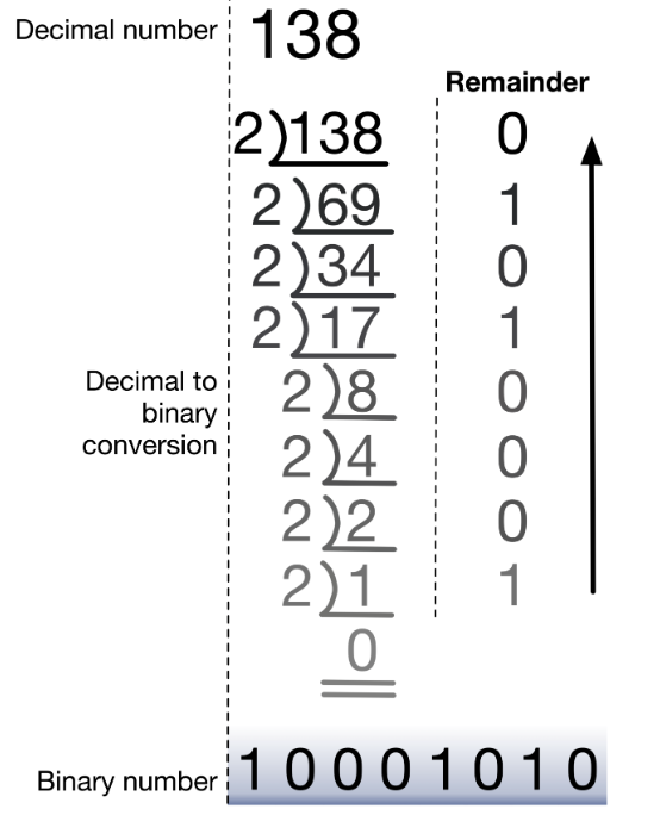
Decimal Number to Binary 十进制转二进制 #
- Decimal Number通过除法的余数得到二进制
Number of Bits to represent x #
- 需要n个二进制位数来表达一个\(2^n\)的Decimal Number
- 要表示 256 个数字,我们需要 8 位。要表示 512 个数字,我们需要 9 位。要表示 1024 个数字,我们需要 10 位
Memory organized way 内存管理方式 #
- Memory通过Cells的方式管理,每一个Cell储存了一个byte 字节
- 而每一个Cell包换他的Address 地址,这使得Mmory Byte 内存字节是Byte-Addressable的
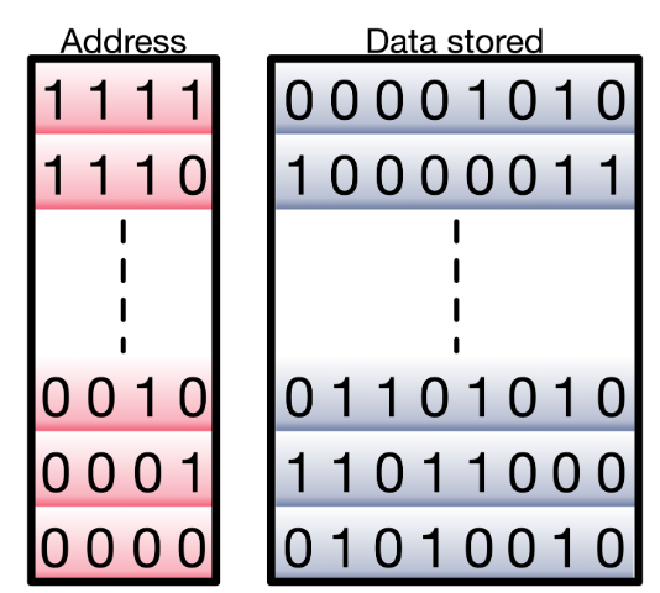
- 当采用32个Bits来表达Cell的Address的时候,我们可以储存\(2^{32}\)个Bytes 字节
- A byte is a group of 8 bits. A kilobyte (KB) is 1024 bytes. A megabyte (MB) is 1024 kilobytes. A gigabyte (GB) is 1024 megabytes. A terabyte (TB) is 1024 gigabytes.
- \(2^{32}\) Bytes也就是4个Gigabytes
- 现代计算机是64-bits的,也就是说它们的Memory Length可以达到\(2^{64}\)位
Hexadecimal & Binary 十六进制和二进制 #
- 已知Hexadecimal和Binary的对应表为
- 0 = 0000, 1 = 0001, 2 = 0010, 3 = 0011, 4 = 0100,
- 5 = 0101, 6 = 0110, 7 = 0111, 8 = 1000, 9 = 1001,
- A = 1010, B = 1011, C = 1100, D = 1101, E = 1110, F = 1111
- 一个Hexadecimal \(c_1c_2\)的本质为\(16^1c_1+16^0c_2\)
- 举例来说一个Hexadecimal \(3A\)的Decimal Number就是\(316^1+A16^0=316+101=58\)
- 更简单的Hexadecimal直接转换到Binary Number的办法就是拼接
- 3 转换为 0011
- A 转换为 1010
- 将它们拼接:3A = 0011 + 1010 = 00111010
1.4 Write Simple C Programs 编写简单的 C 程序 #
// This program prints the message "Hello World!" on the screen.
##include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
printf("Hello World!\n");
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>允许访问与输入(如键盘)和输出(如监视器)设备接口的功能。这些函数包括 和 。printf``scanfmain是 C 程序的入口点。所有 C 程序都需要 main 函数- 在执行程序时调用。它返回一个整数值。该值表示程序执行成功。任何其他值都表示程序失败
printf是将字符串打印到屏幕的函数\is called an escape character 转义字符 ,\nis a special character that indicates a new line
Input 输入 #
##include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
int numPizzas, numSlices;
printf("How many pizzas do you have?\n");
scanf("%d", &numPizzas);
numSlices = numPizzas * 8;
printf("You have %d slices in %d pizza.\n", numSlices, numPizzas);
return 0;
}
int numPizzas, numSlices;声明两个类型的变量intis a data type that represents integersscanf("%d", &numPizzas);将获取用户输入并将其分配给 variable&Address-of Operator(取地址符) 是为了将变量的地址传递给scanf
pass-by-value 按值传递 #
在 C 语言中,函数的参数传递默认是按值传递(pass-by-value)。这意味着:
- 当你调用一个函数时,传递的实际上是变量值的副本,而不是变量本身。
- 因此,如果不通过地址传递,函数无法直接修改原始变量的值。
Escape Sequences 转义序列 #
- 转义字符是由反斜杠
\开头的一组特殊字符,用于表示一些特殊含义。 \n表示换行。\t表示制表符。\\表示反斜杠本身。\"表示双引号。