Last Edit: 9/23/24
Plastice Deformation (Permanent Deformation) #
- we use the term plastic to describe permanent deformation
- 之所以是Plastic,是因为它derives from the Greek plastikos meaning to sculpt
Changes After Plastic Deformation #
- 在Plastic Deformation后,Atomic Spacing将保持\(r=r_0\)
- 但是Sequence of atoms将进入一个New Equilibrium
- 即在Marcro Perspective上发生Shape的Deform
- Tensile Strain将会保持一定非零大小
Micro Perspective of Plastic Deformation #
Different between Elastic and Plastic Deformation #
Elastic #
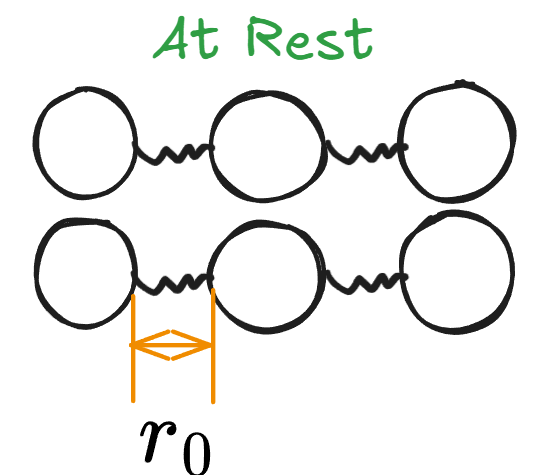
- 对于Elastic Deformation,开始前物理Atom之间间距应为\(r_0\)
- 泄力后仍应该是\(r_0\),并且Atom将会到他们原有的Equilibrium
- 并且物体从Marco Perspective上并不发生Deformation
Plastic #
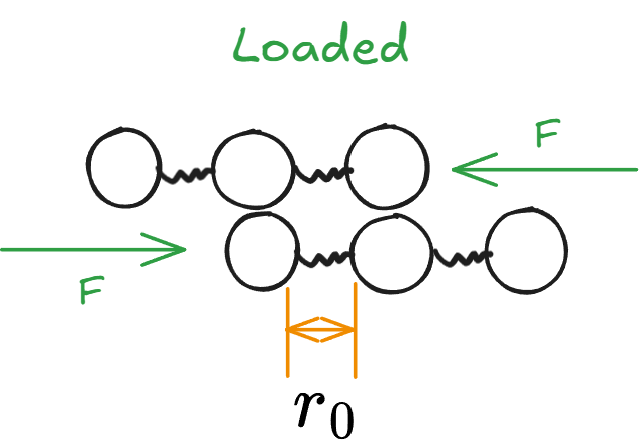
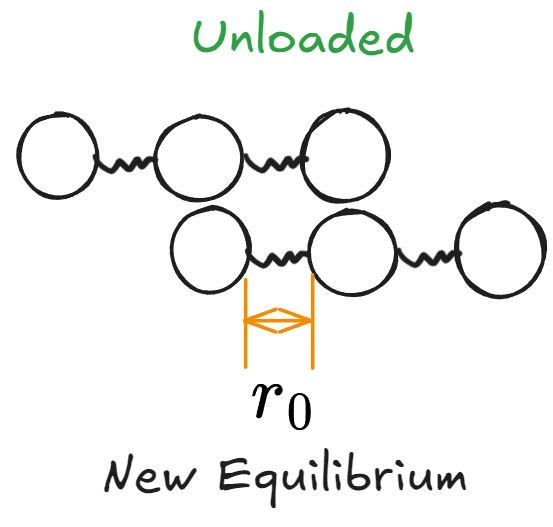
- 结束后Atom之间间距仍应该是\(r_0\)
- 泄力后Atom将进入一个新的Equilibrium
- 物体在泄力后,他的Tensile Strain将不会便为0而是保持在一定数
- 即Shape已经发生了Perminant Change
Beyond Elastic Region #
- 在Elastic Region外,便是完整的[[ECMS 2. Elastic Behavior#Young’s Modulus 杨氏模量]]的模型
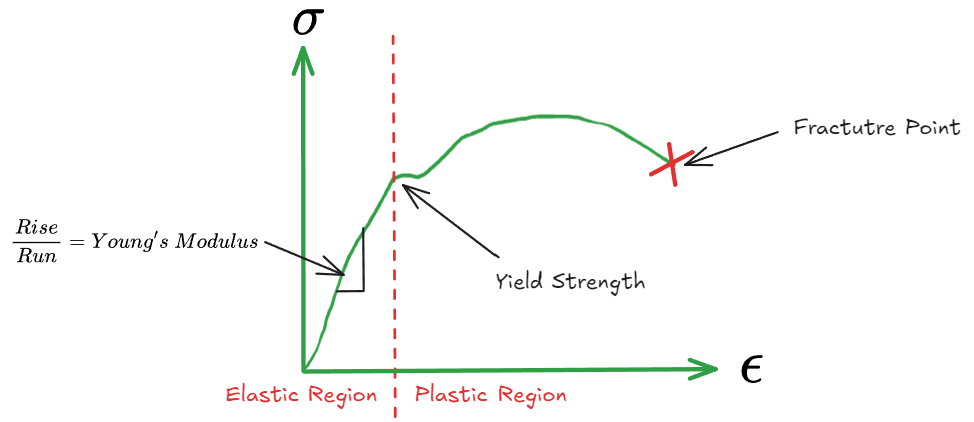
- Yield Strength: 屈服强度是指材料在发生永久变形之前,能够承受的最大应力。
- 当Strain到达Yield Strength之后,材料会从Elastic Deformation转变为Plastic Deformation,即Material发生Permanent Deformation
- 在过了Yield Strength之后Strain再增加后到了一定程度之后便会产生Fracture(Broken into pieces)
Stress-Strain Curve for different materials #
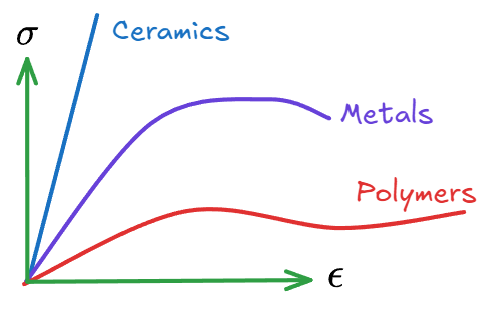
Metals #
- 图中的绿色曲线
- 其特点有在一定位置之后开始产生Permanent Deformation
- 之后在持续的施加Stress之后其Strain变化率降低最后产生Fracture
- 相比于Ceramic和Polymer,其Young’s Modulus处于中间位置,高于Polymer但小于没有Permanent Deformation阶段的Ceramic
Polymer #
- 相对来说没有什么特点
- 具有较低的Young’s Modulus和Permanent Deformation区间
Ceramic #
- 对于陶瓷类的物质,其没有Permanent Deformation的区间
- 对于他来说也存在Elastic Region
- 但可以看出整体Young’s Modulus非常高,并且呈现线性
- 在施加了一定的Stress后会直接Load enough and fracture
Three-Point-Blending Test #
- 底部两个点用作支撑,上方一个力将物体往下压
$$Stress(\sigma)=\frac{3FL}{2wh^2}$$
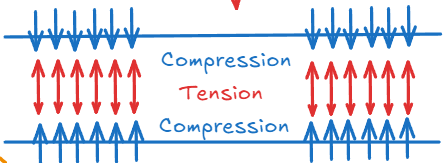
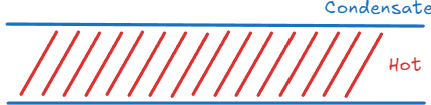
Tempered Glass 钢化玻璃 #
![[ECMS 3. Plastic Deformations-5.png]]
- 再高温下迅速向表面喷冷凝液将其降温
- 冷却将使玻璃表面收缩的比内部更快,产生了向心的Compress Stress
- 而内部由于受力将产生反作用力,向外产生张应力
- 整体的结构处于一个向内部收缩的趋势,导致当其受到了外力的时候,尝试使其Fracture的导致分子之间结构被破坏的力将被抵消
- 并且由于其内部存在Residual Stress(残余应力)导致了整体结构破坏的时候其Residual Stress将破坏结构至非常小的结构