Last Edit 9/24/24
Hooke’s Law #
$$F=kx$$
- Spring constant (k): Spring Constant
Material properties(材料性能) #
- 主要指材料的基本机械性能,如弹性模量、屈服强度、抗拉强度等
- 它们的计算方式应当剔除几何尺寸的影响
Stress 应力 #
- 物体在外力作用下,单位面积上承受的内力 $$Stress(\sigma)=\frac{F}{A_0}$$
- \(A_0\): Initial Cross-Sectional Area
- 应力的单位通常是帕斯卡(Pa)
Strain 应变 #
- 应变是材料在外力作用下发生的变形程度
$$Strain(\epsilon)=\frac{\Delta l}{l_0}$$
- \(\Delta l\):change of material’s length
- \(l_0\): Initial length of material
Young’s Modulus 杨氏模量 #
-
是固体在载荷下的刚度或对弹性变形的抵抗力的量度
-
材料在压缩或拉伸时会发生Elastic Deformation,而在Unloaded之后则会回到之前的Equilibrium $$E=\frac{\sigma}{\epsilon}=\frac{\frac{F}{A_0}}{\frac{\Delta l}{l_0}}=\frac{F\cdot l_0}{A_0\cdot \Delta l}$$
-
Young’s Modulus (E)
-
单位是Pa
Structure Independent #
- 当说"XXX is xxx independent" 时,代表了某个事物不依赖于某个特定因素
- 这里则是Young’s Modulus是不依赖于Structure
- Young’s Modulus其只与材料有关,与形状无关
- 具体来说是取决与材料的原子级别的相互作用,而不是材料的宏观或微观结构
Micro Perspective of Stress and Strain #
- 从微观角度来看,物体由Atoms组成,其中存在Inter Atomic Forces
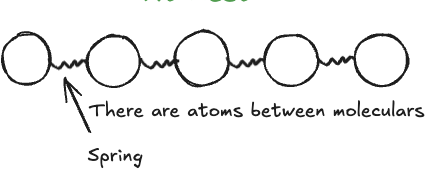
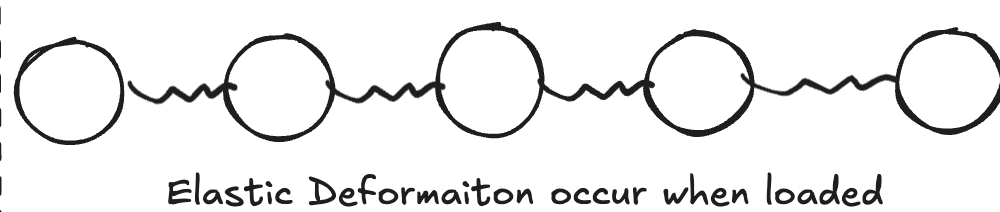
- 当Applied External Force的时候,物体将处于Loaded状态,其Shape将会发生改变
- 具体来说,Shape发生的改变是由于Atoms之间的间距发生了改变
- 不过只要整个Stress小于Yield Strength,所有的Deformation都将是Elastic的
- 代表了,当External Force被撤去的时候,既Unloaded之后,Atoms将会回到他们原来的Equilibrium position
- 需要注意的是,Atom之间的间距将会回到一开始的\(r=r_0\)
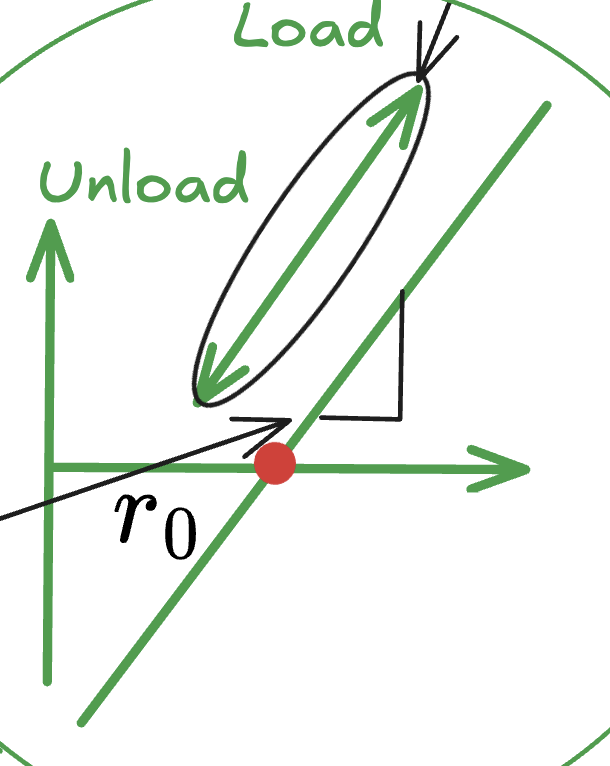
- 所以可以得出一个结论:Elastic Strain is Reversible
Stress-Strain Curve 应力-应变图 #
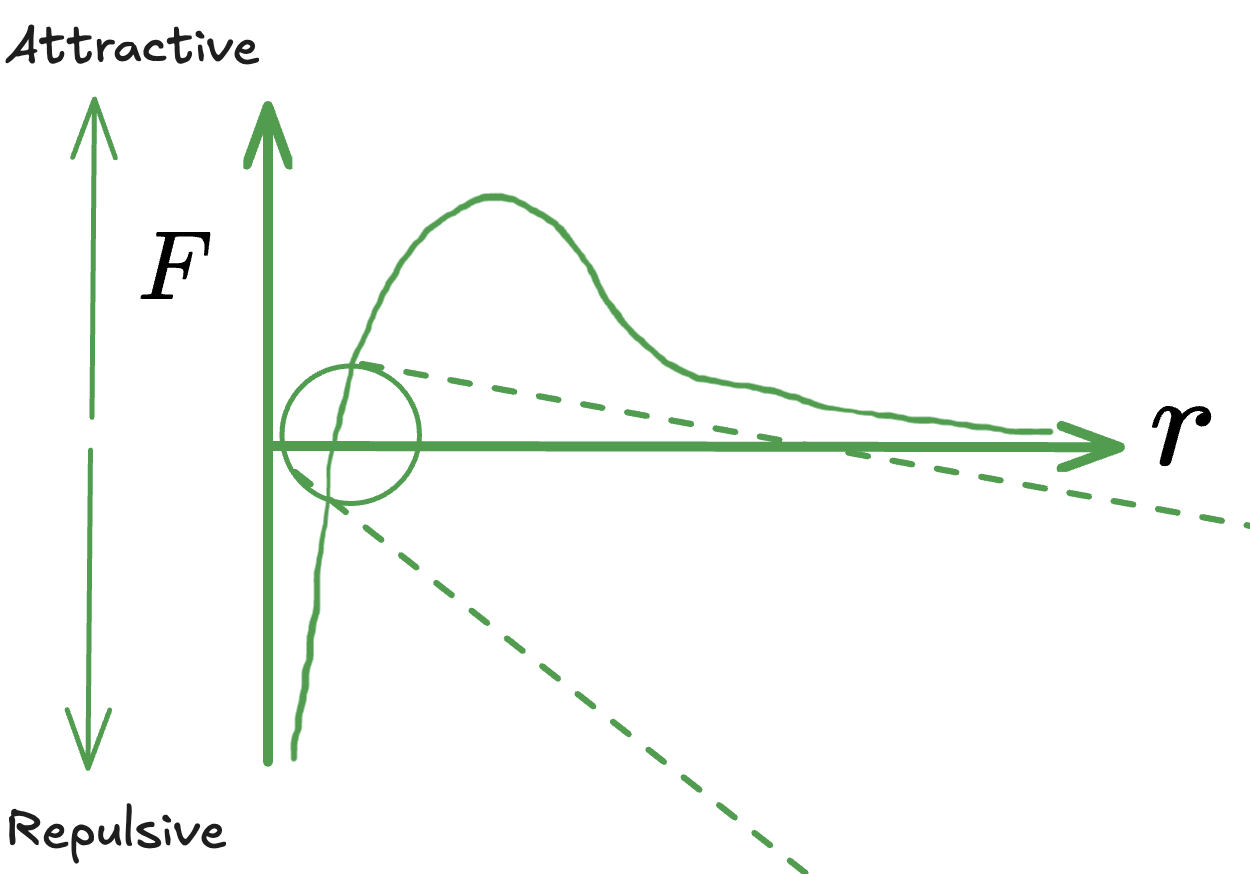
本图实际上为F-r图,即拉力-原子间半径图,但与Stress-Strain图相似,便用SS图讲解
- 对于一个材料,在对其施加Stress的时候,其Strain会出现如此的固定趋势
- 在Stress等于0的时候,物体处于Equilibrium状态,具体来说其Attractive Force = Repulsive Force
- 在持续施加Stress后,Atoms最终将到达一个Yield Strength(不可逆点)后将会产生Plastic Deformation(将在下一章提到)
- 将Stress-Strain图放大到\(r_0\)两边后观察
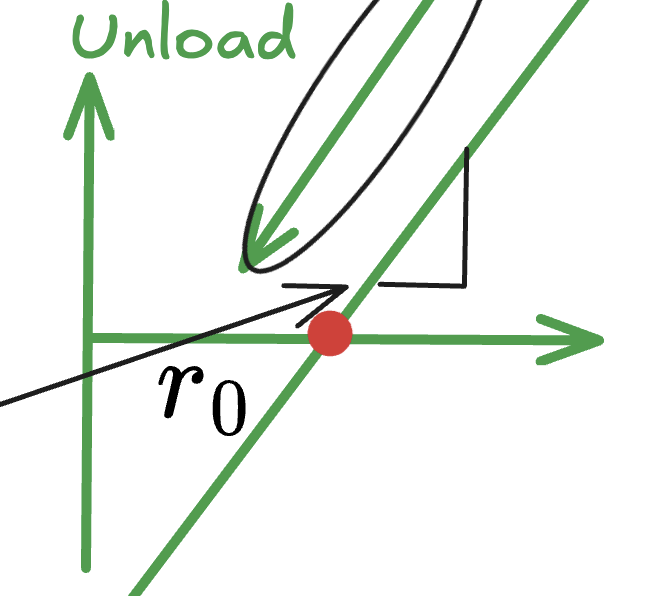
- 可以发现Stress随Strain(Atomic Spacing)基本呈现Linear Trend,便可以说 $$E\propto \frac{dF}{dr}|_r=r_0$$
- Young’s Modulus is directly propotional to slope of interatomic force speration curve at equilibrium spacing
- 简单的理解便为:杨氏模量等于与Stress对于Strain的变化率
- 更具图可以看出Stress对Strain的变化速率越大,其Young’s Modulus越大
- 即在Plastic Deformation前,Stress(External Force)越大材料的Young’s Modulus越大
- 既抵抗Elastic Deformation的作用越大
The way to determine material properties #
Tensile(Tension) Test
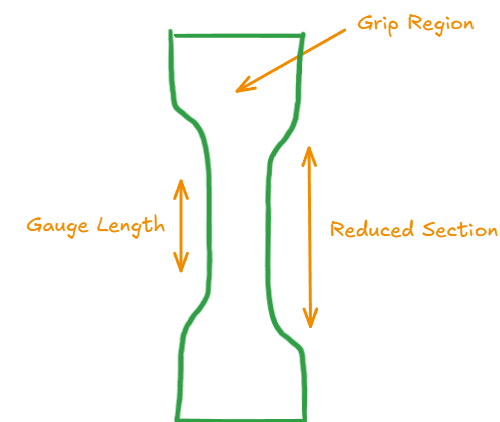
- 图中展示了拉伸测试的基本原理,即通过对材料施加拉力(Tension),使其伸长(elongating),从而获得应力-应变曲线等相关数据
- Grip Region(夹持区):这是样品被测试机夹持的地方,两端施加拉力
- Reduced Section(缩小部分):这是样品的中间区域,它的截面积被减少,以确保样品在这个区域发生断裂或变形。在该区域内,材料会受到均匀的拉伸应力。
- 通过拉伸测试,可以获得材料的关键参数,如杨氏模量 (Young’s Modulus)、屈服强度 (Yield Strength)、极限抗拉强度 (Ultimate Tensile Strength, UTS) 和断裂延伸率 (Fracture Elongation)
Disadvantage of Tensile Test #
- 这种测试方法仍然存在局限性,例如Ceramics & Glasses等都不能利用这种方式测试Material Properties,具体来说
- Low strain to fracture, almost no deformation before breaking:在断裂之间,几乎不发生Elastic Deformation
- hard to grip:对于Tensile Test所必须的Grip Region,由于一些Material的特殊性,他们无法在Grip Region内被夹住,继而无法进一步测试
- Hard to load on Axis: 当Grip Region滑动的时候,无法使力沿轴拉伸
- 关于为什么这些会发生,如为什么Ceramics会直接断裂等,参考[[ECMS 3. Plastic Deformations]]