Last Edit: 1/8/25
10.1 Parametric Equations #
- If x and y are continuous functions of t on an interval I, then the equations are called parametric equations and t is called the parameter $$x=x(t) andy=y(t)$$
Eliminating the Parameter 化简 #
- 通过关系式直接得到x和y之间的函数
ex. #
$$x(t) = t^2 - 3, \quad y(t) = 2t + 1, \quad -2 \leq t \leq 3.$$
- 从第二个Equation中提出\(t = \frac{y - 1}{2}\)后带入 $$x = \left(\frac{y - 1}{2}\right)^2 - 3 \ = \frac{y^2 - 2y + 1}{4} - 3 \ = \frac{y^2 - 2y - 11}{4}$$
Use Trigonometrey to Eliminate Parameter #
- 通过一些等式建立x和y之间的关系
- 例如\(\cos^2x+\sin^2 x=1\)
ex. #
- 有\(x = 3 \cos \theta \quad \text{and} \quad y = 4 \sin \theta, \quad 0 \leq \theta \leq 2\pi\)
- 通过\(cos \theta=\frac{x}{3},sin\theta=\frac{y}{4}\)替换原式,便有\((\frac{x}{3})^2+(\frac{y}{4})^2=1\)
10.2 Calculus of Parametric Curves #
Derivatives of Parametric Equations #
- If a smooth curve C is given by the equations $$x = f(t) \quad \text{and} \quad y = g(t)$$
- then the slope of C at (x, y) is $$\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{\frac{dy}{dt}}{\frac{dx}{dt}}, \quad \frac{dx}{dt} \neq 0 $$
Arc Length of a Parametric Curve #
- 普通的Arc Length公式为\(\int^b_a\sqrt{1+[f’(x)]^2}dx\)
- 将Parametric Curve的Derivative带入,得到 $$\int^b_a\sqrt{1+(\frac{dy/dt}{dx/dt})^2}dx=\int^b_a\sqrt{\frac{(dx/dt)^2+(dy/dt)^2}{(dx/dt)^2}}\frac{dx}{dt}dt$$
- 也就是 $$=\int^b_a\sqrt{(\frac{dx}{dt})^2+(\frac{dy}{dt})^2}dt=\int^b_a\sqrt{[f’(x)]^2+[g’(t)]^2}dt$$
10.3 Polar Coordinates 极坐标
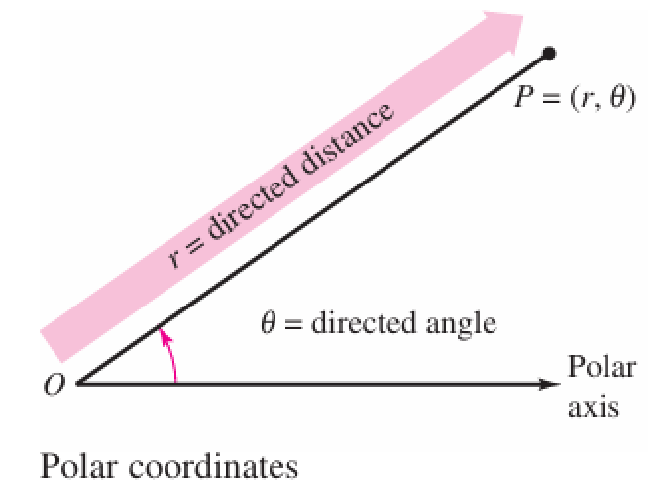
- Polar Coordinates,一个新的坐标系,通过Radius和于Polar Axis的Directed Angle来表示点在坐标系中的位置
Converting Points between Coordinate Systems #
- 想要把Cartesian Coordinates转换为Polar Coordinates,只需要找到\(r=\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\) 和 \(\tan^{-1}\frac{y}{x}\)便可
- 而Polar 到 Cartesian的转换则是通过公式\(x=r\cos\theta , y=r\sin\theta\)得到
10.4 Area and Arc Length in Polar Coordinates #
Slope of Polar Curve #
- 对于Polar Coodinates来说,其Derivative可以通过一个简单的Chain Rule得到 $$\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{\frac{dy}{d\theta}}{\frac{dx}{d\theta}} = \frac{f(\theta) \cos \theta + f’(\theta) \sin \theta}{-f(\theta) \sin \theta + f’(\theta) \cos \theta}$$
Areas of Regions Bounded by Polar Curves #
- 在之前都是采用多边形来近似面积,而在Polar Region中,采用了扇形的来近似
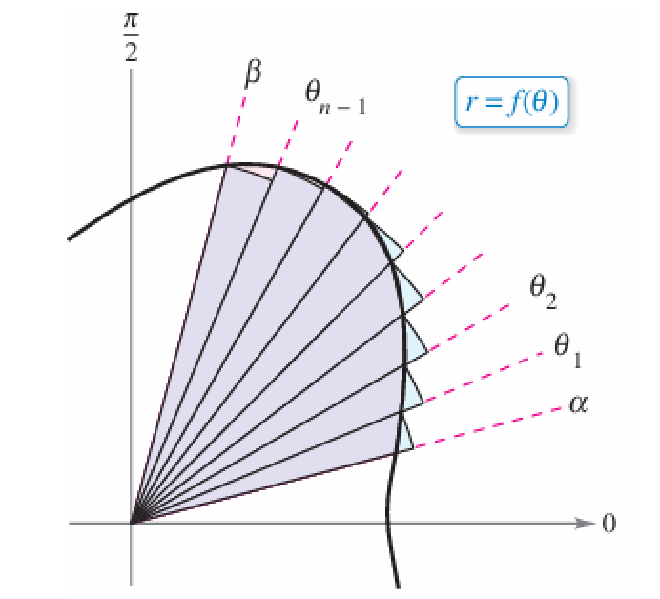
$$A = \lim_{n \to \infty} \frac{1}{2} \sum_{i=1}^{n} [f(\theta_i)]^2 \Delta \theta = \frac{1}{2} \int_{\alpha}^{\beta} [f(\theta)]^2 d\theta$$